3D Navigation: Understanding Global, Local, and View Axes
Share:
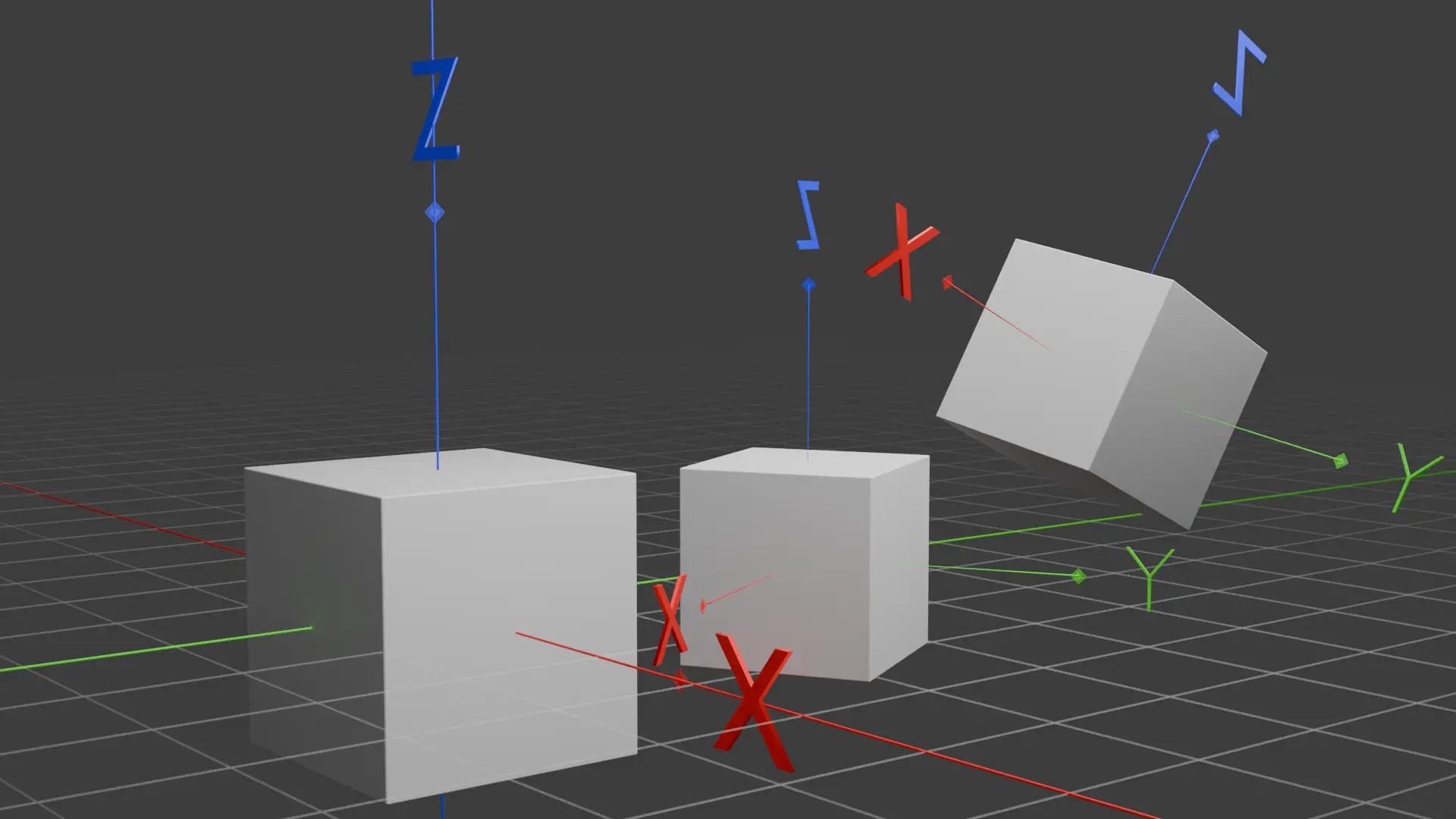
Have you ever wondered how 3D navigation works in virtual environments? Understanding the various axes can help you navigate and interact seamlessly within a three-dimensional space.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Introduction:
In the world of 3D navigation, understanding the different axes is crucial for accurate and efficient movement within a three-dimensional space. In this article, we will dive into the concepts of global, local, and view axes, highlighting their differences and applications in various scenarios.
What are 3D Axis?
In 3D navigation, axes are used to define spatial orientation and movement within a three-dimensional environment.
Each axis represents a different direction along which an object or viewer can move.
The three main axes are X, Y, and Z, with X representing left and right, Y representing forward and backward movement, and Z representing up and down.(as in blender and it’s different in other programs)
Global Axis
Global axes refer to the fixed coordinate system of a 3D space. These axes are consistent and do not change regardless of the object’s orientation or position within the environment. The global X-axis points to the right, the Y-axis points forward, and the Z-axis points upward. Global axes are used as a universal reference point for positioning and navigating objects within a 3D space.
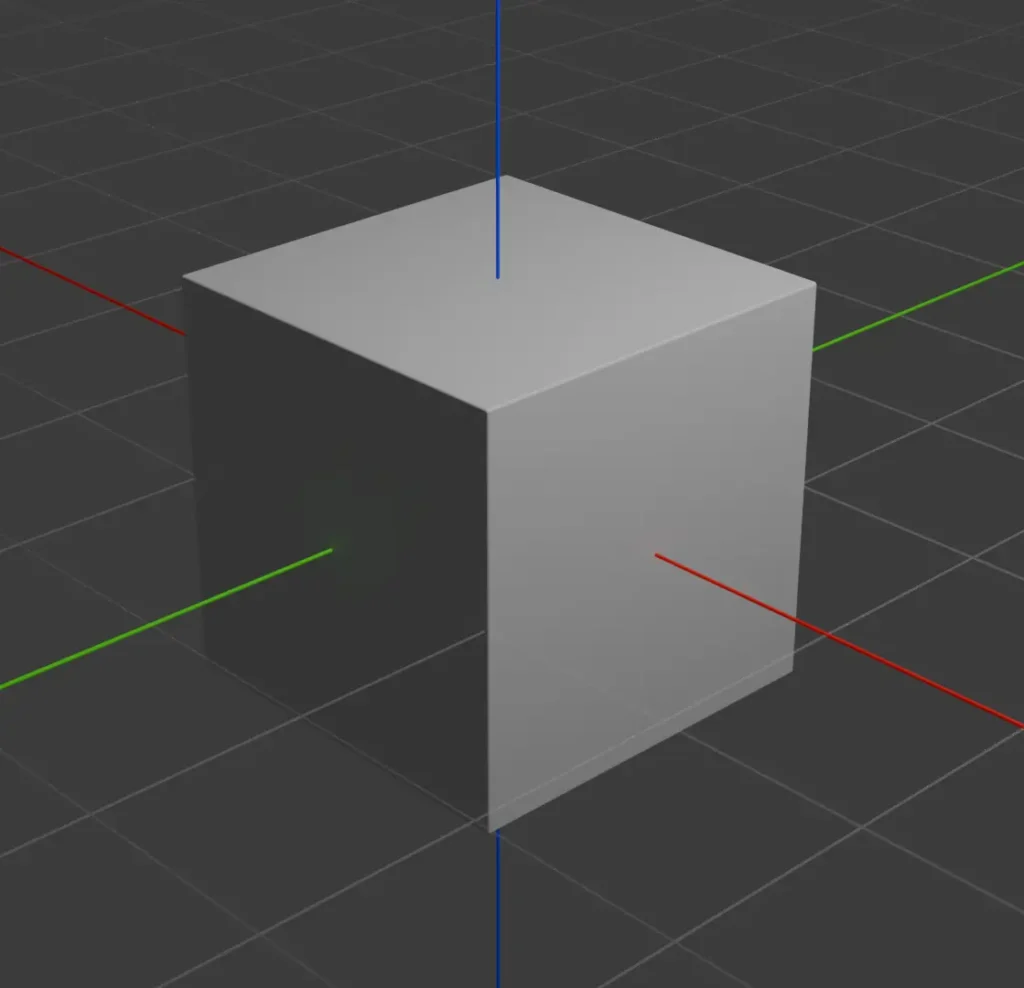
Local Axis
Local axes are specific to an individual object within a 3D environment. Unlike global axes, which are consistent for all objects, local axes are relative to the orientation of the object itself. As the object rotates or moves within the space, its local axes adjust accordingly. Local axes are useful for manipulating and controlling the movement of individual objects independently of each other.
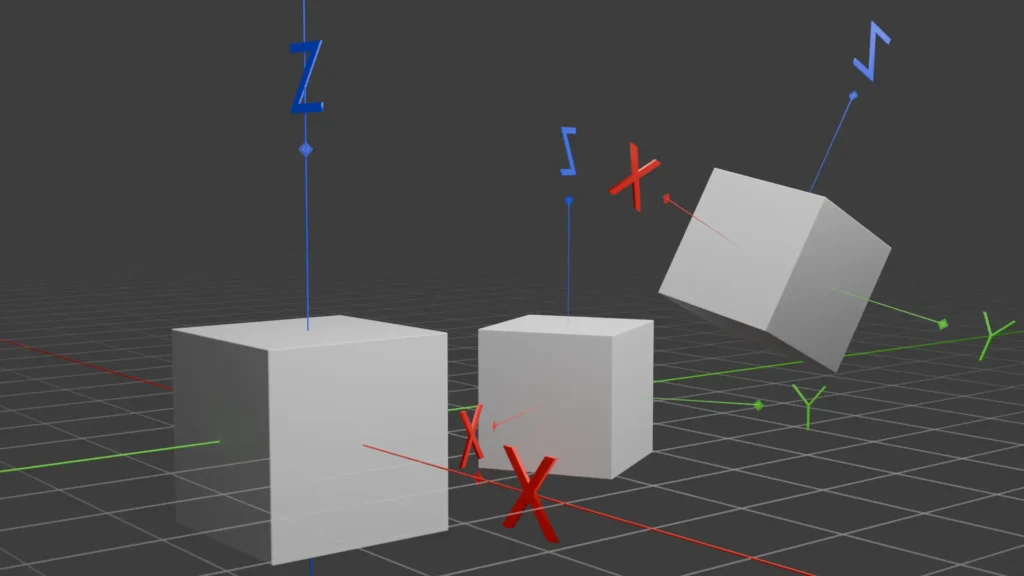
View Axis
View axes are tied to the perspective of the viewer within a 3D environment. These axes change dynamically based on the viewer’s position and orientation in relation to the objects in the scene. View axes allow for a realistic and immersive experience by adjusting the orientation of objects based on the viewer’s perspective. They play a crucial role in creating engaging and interactive virtual environments.
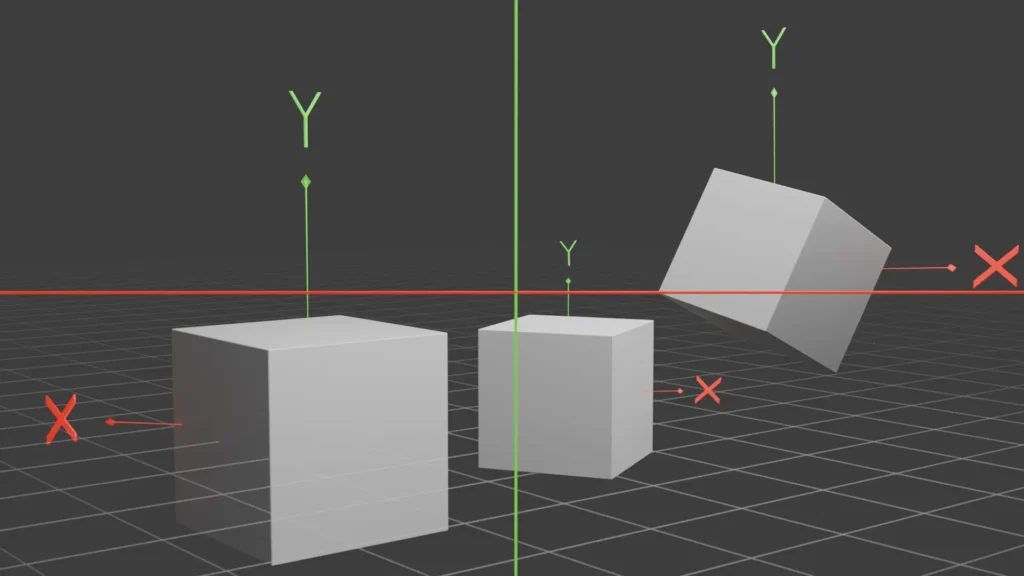
Normal Direction
Normal(s) is a term used to define face/vertex direction as the Z axis is perpendicular to the face, X axis face’s right and left and Y axis being forward and backward.
An application for it would be moving, extruding faces with weird angles
Application of Different Axes
Global axes: moving objects into the same direction no matter them directions are.

Local axes: rotating objects in the same time on them own Y local axes to make them vertical.
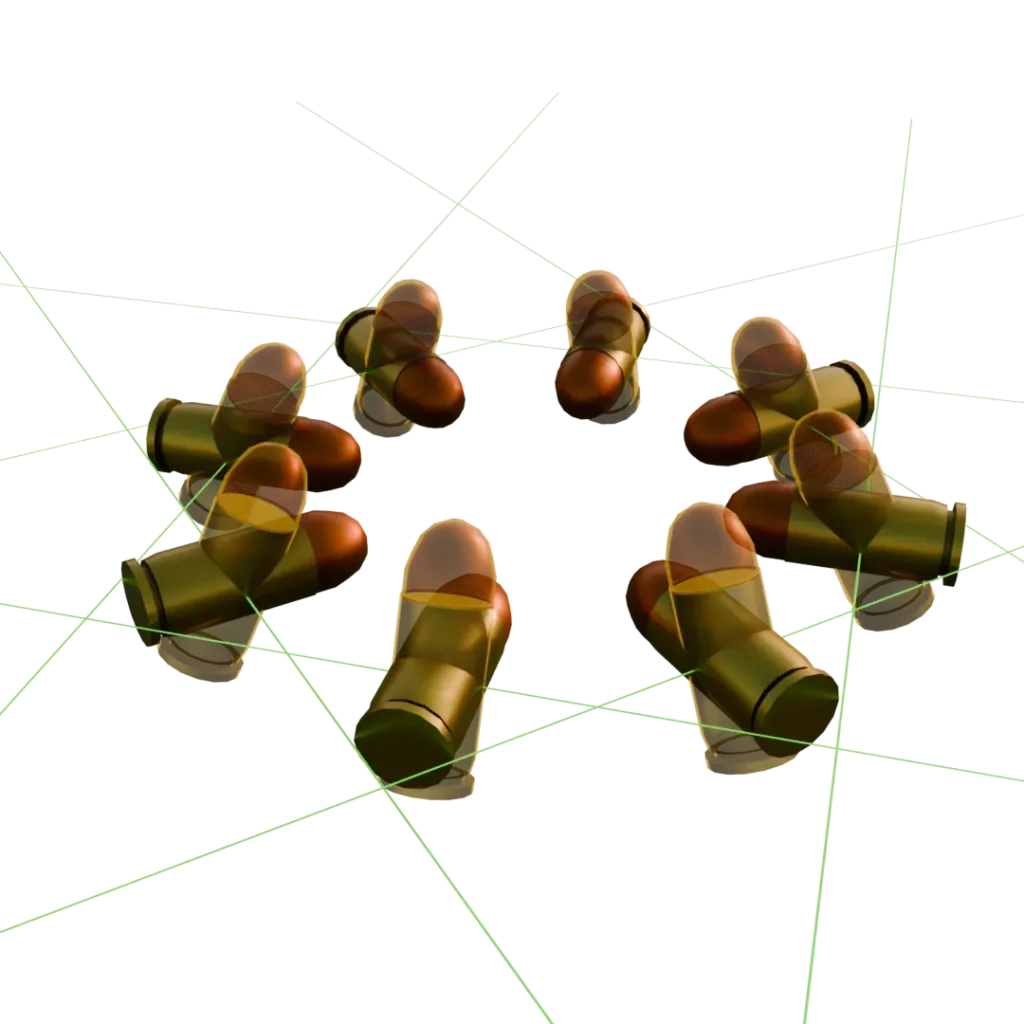

View: distributing assets from the camera view.

Normal: extending tilted face on it’s direction
In conclusion, understanding the differences between global, local, and view axes is essential for mastering 3D navigation. By leveraging the unique characteristics of each axis.





